Sciatica
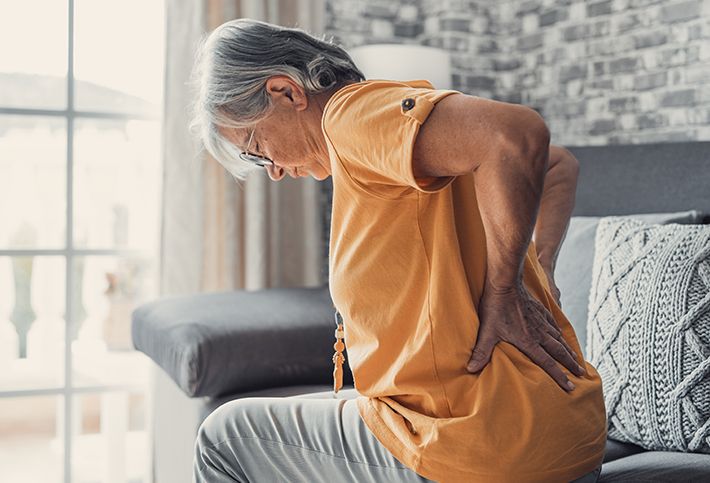
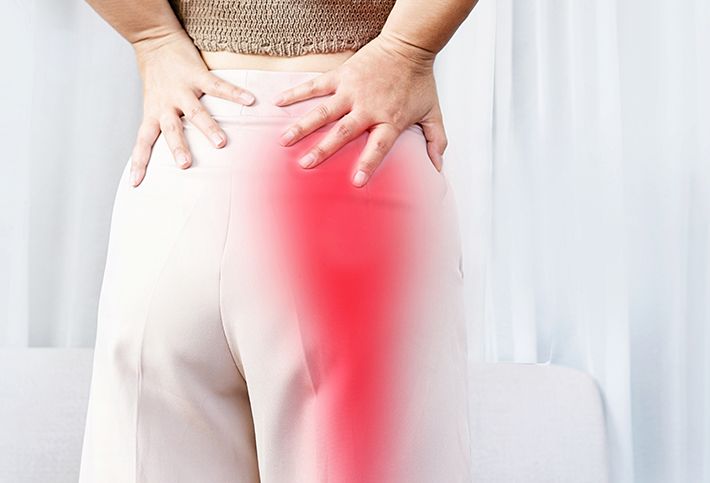
Sciatica is an irritation of the sciatic nerve, causing dull, shooting, or aching pain that starts in the lower back and/or the buttocks and radiates down to one of the legs. Depending on its cause, sciatica can heal on its own over time. However, more serious causes may require medical treatments, ranging from non-surgical to surgical methods.